井上研究室
研究テーマ
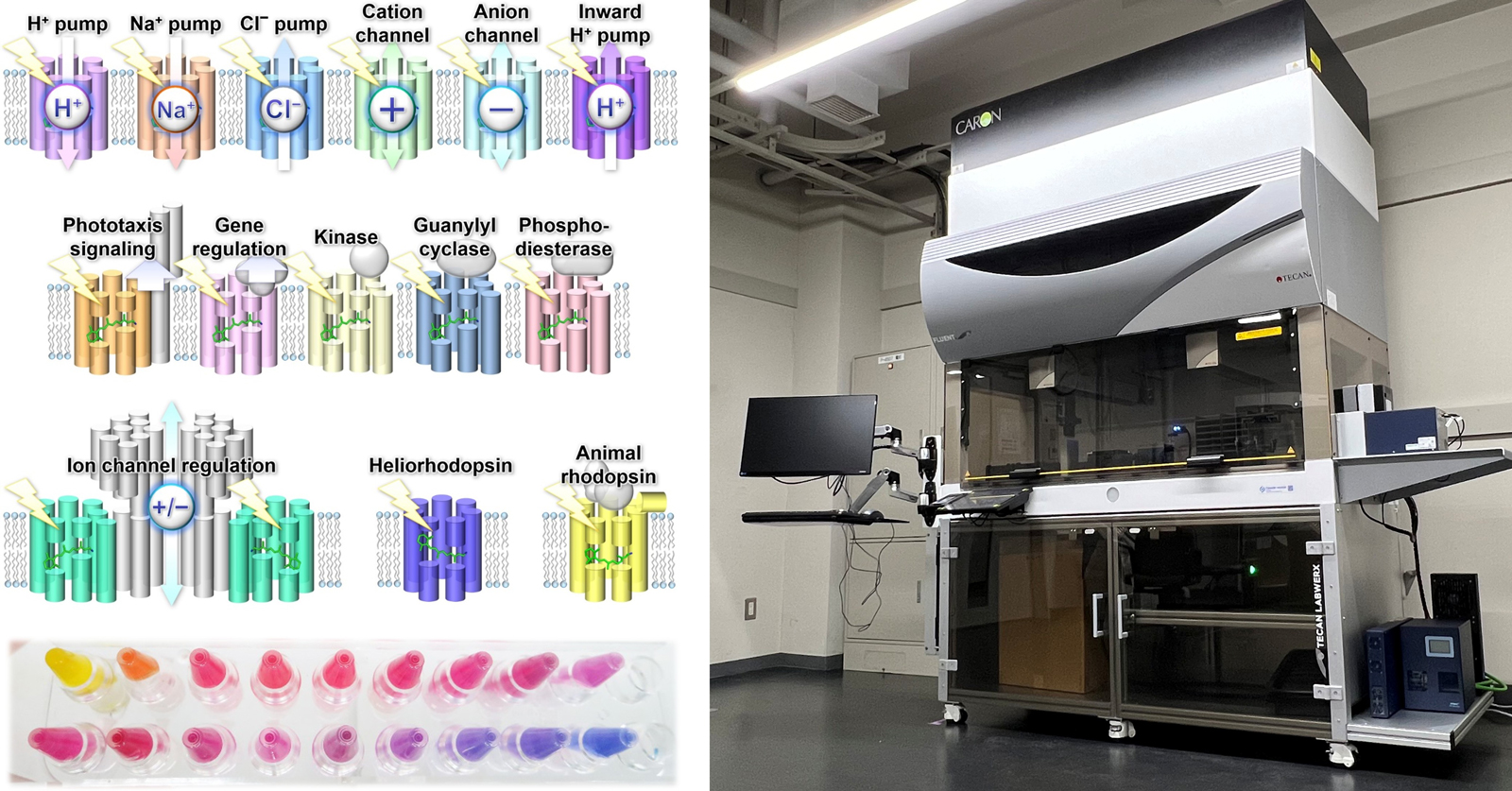
- 光受容型膜タンパク質ロドプシンの分子機能メカニズムの機能解析および分光研究
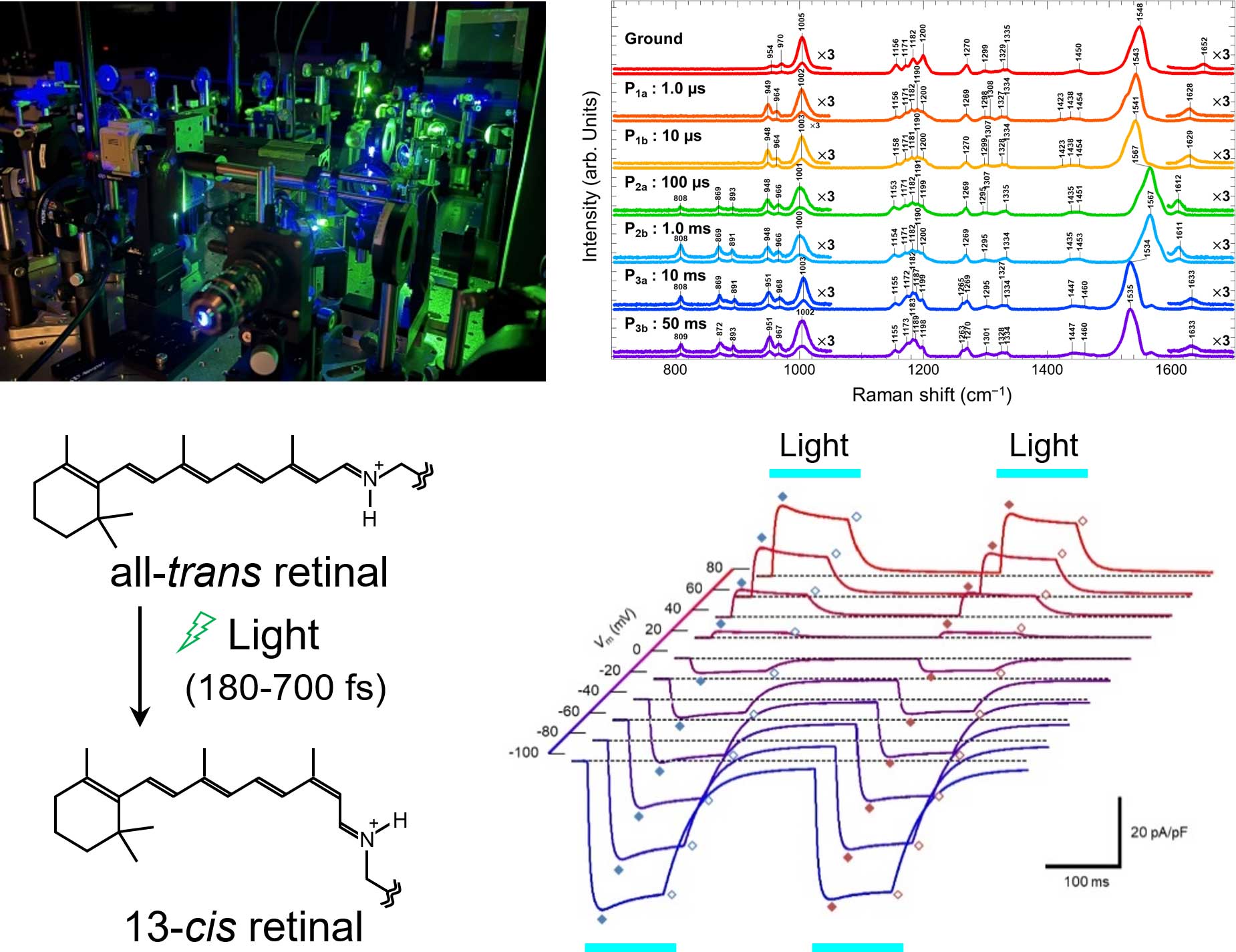
- 先端的分光計測法の生体分子研究への応用
- ゲノムビッグデータをもとにした新奇光受容型タンパク質探索
- 機械学習法と実験自動化を用いた生体分子の機能決定因子の解明とそれにもとづく新規機能性分子開発
多くの生物は太陽光を、自身の生理活動のためのエネルギー源や、外界の環境変化を知覚するための情報源として利用する。そしてこのときに中心的な役割を果たすのが、多様な光受容タンパク質である。
本研究室では、それら多様な光受容タンパク質の機能発現メカニズムを統一的に明らかにすることを目的とし、レーザー時間分解分光実験や振動分光実験などを通じて、高次複雑系である光受容タンパク質分子の化学反応素過程を調べる研究を行っている。さらに電気生理学実験や、生化学的手法と組み合わせることで、原子・分子レベルから細胞・個体レベルにおよぶ多階層的な理解を目指している。そして、これらの知見をもとに、光遺伝学などの応用を目標とした機能性生体分子の開発にも取り組む一方で、近年の急速なゲノム解析技術の発展がもたらすゲノムビッグデータをもとに、新奇な光生物学的現象とそれに関わる分子群の探索研究や機械学習法ならびに実験自動化法の開発を行っている。