Ferrimagnetic Compensation and its Thickness Dependence of TbFeCo Alloy Thin Films
Nakatsuji Group
Rare earth (RE)-transition metal (TM) ferrimagnetic materials have compositions in which the antiferromagnetically coupled magnetization of RE and TM atoms compensates, resulting in a zero net magnetization. Tuning magnetization to zero is particularly advantageous in creating efficient memory devices based on magnetic materials. Moreover, such materials exhibit bulk perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), whose origin is different from the interfacial PMA. This property offers another advantage for applications. This study reports a systematic investigation into the magnetic properties of ferrimagnetic TbFeCo thin films deposited on a Pt underlayer. Our results show that the Tb concentration, at which magnetic moments of Tb and Fe or Co sublattices are compensated, increases with the thickness of TbFeCo thin films because the Tb atoms are magnetically inert as they are mixed with the Pt underlayer (Fig. 1). Furthermore, we clarify the relationship between the loss of magnetism of Tb atoms and bulk PMA. This study provides a prospect for designing ferrimagnetic ultrathin films with large PMA, which is essential for fabricating magnetic memory devices.
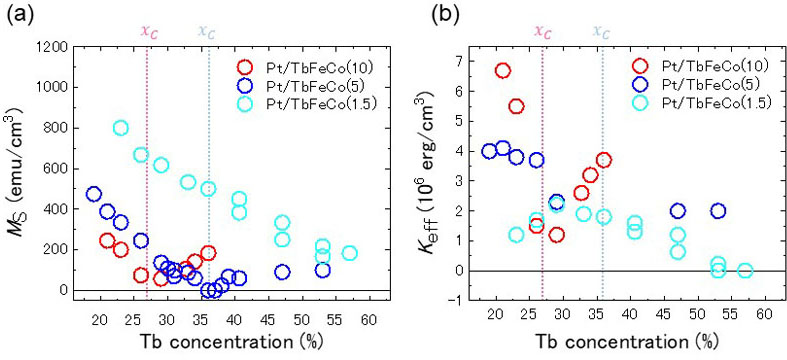
Fig. 1. (a) and (b) Tb concentration dependence of the saturation magnetization MS (a) and the effective magnetic anisotropy energy density Keff (b) for TbFeCo thin films with different thicknesses. The underlayer is Pt. Red circles: Pt/TbFeCo(10 nm), blue circles: Pt/TbFeCo(5 nm), and light blue circles: Pt/TbFeCo(1.5 nm). Red and blue broken vertical lines denote the compensation composition xc for Pt/TbFeCo(10 nm) and Pt/TbFeCo(5 nm), respectively.
References
- [1] M. Ishibashi, K. Yakushiji, M. Kawaguchi, A. Tsukamoto, S. Nakatsuji, and M. Hayashi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 120, 022405 (2022).
