Heavy electrons in strong magnetic fields, reveal electronic state of Kondo insulator YbB12 in magnetic fields
The University of Tokyo
Ibaraki University
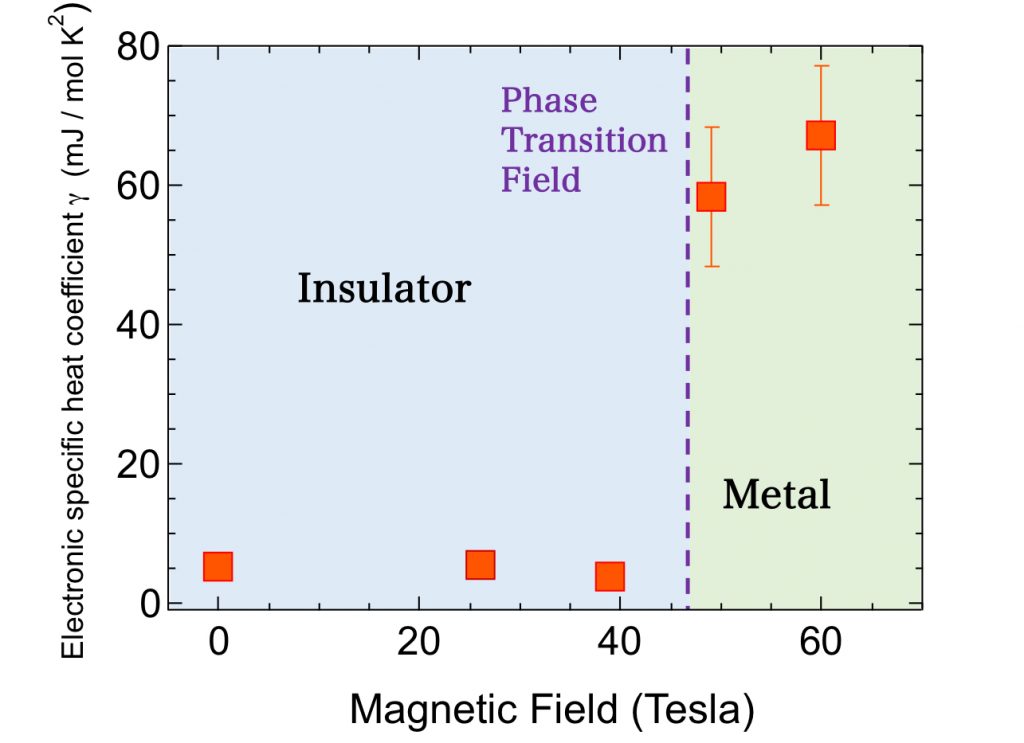
The research found electrons in the strong magnetic field metal phase were tens of times heavier than usual electrons, when the specific heat of Kondo insulator YbB12 (12 ytterbium boride) was measured at up to 60 T. This experiment was conducted by the research group of associate professors Yasuhiro Matsuda and Yoshimitsu Kohama at the Institute for Solid State Physics, the University of Tokyo, together with professor Fumitoshi Iga of the College of Science at Ibaraki University and others. The result directly suggests significant Kondo effects, which is a typical many-body electron correlation effect.
Although research for Kondo insulator has been continued for more than half a century since the 1960’s, elucidation of the mechanism for converting it into insulator was not enough due to strong electron correlation effects. Since new concepts such as topologicality and neutral Fermionic particles have been proposed, a big interest is expressed. As such, the group demonstrated the hidden metal state of this substance had strong Kondo effects for the first time.
This finding gives a new understanding to the role of Kondo effect in both the challenges the old and new solid state physics face on the difference between insulator and metal means. The Kondo effect is a typical many-body electron correlation effect and is important tool in realizing non-conventional superconductivity and mesoscopic quantum fluctuations. The results of this research will greatly contribute to the understanding for a broad ranging substance systems including these all.
The research article was published in Physical Review Letters, the bulletin of American Physical Society (June 22, 2018).
Reference:
- Journal: Physical Review Letters
- Title: Magnetic-field-induced Kondo metal realized in YbB12
- Authors: Taku T. Terashima, Yasuhiro H. Matsuda*, Yoshimitsu Kohama, Akihiko Ikeda, Akihiro Kondo, Koichi Kindo, Fumitoshi Iga
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.257206
