Hall Coefficient of Fe-based Superconductor Ba1-xKxFe2As2
Ohgushi Group
We have investigated the normal-state properties of the Fe-based superconductor Ba1-xKxFe2As2 by means of the Hall coefficient (RH) measurements. RH displayed in Fig. 1 exhibits a significant variation as a function of x and temperature (T). At x = 0, a negative RH gradually increases in magnitude on cooling, shows a discontinuous jump at the Néel temperature, and reaches a constant value at 5 K. When holes are doped, RH changes its sign. In a wide T range, RH still shows a monotonic increase in magnitude on cooling; however, such a tendency becomes more moderate with increasing x. For 0.45 ≤ x ≤ 0.55, we found a crossover phenomena from the high-T increasing to the low- T decreasing behavior in RH at T ~ 100 K, which is indicated by triangles in Fig. 1.
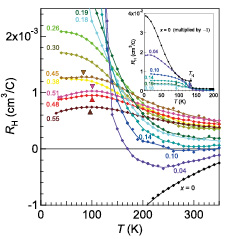
Fig. 1. Temperature (T) dependence of the Hall coefficient (RH) for Ba1-xKxFe2As2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.55). The triangles indicate the crossover temperature, where RH turns to a decrease on cooling. The inset shows RH for samples which undergo the antiferromagnetic transition at low T in a full scale. The arrows indicate the antiferromagnetic transition temperature. Note that the data for x = 0 is multiplied by -1.
In order to interpret these complicated behaviors, we analyzed the data on the basis of the Boltzmann equation for a two-band system with a rigid-band approximation. We then got the following knowledge. (1) Holes with heavier mass at the Brillouin zone center feel less dissipation than electrons at the Brillouin zone corner. (2) Antiferromagnetic fluctuations, which can be monitored by a gradual increase of | RH | on cooling, gradually weaken with a departure from the antiferromagnetic phase in the x-T plane. (3) An anomalous coherent state characterized by heavy quasiparticles in hole bands evolves below T ~ 100 K, predominantly in the optimal and overdoped regions; this phase has a close connection with the pseudopeak observed in angle-resolved photoemission spectra [2].
References
- [1] K. Ohgushi, and Y. Kiuchi, Phys. Rev. B 85, 064522 (2012).
- [2] T. Shimojima, F. Sakaguchi, K. Ishizaka, Y. Ishida, T. Kiss, M. Okawa, T. Togashi, C.-T. Chen, S. Watanabe, M. Arita, K. Shimada, H. Namatame, M. Taniguchi, K. Ohgushi, S. Kasahara, T. Terashima, T. Shibauchi, Y. Matsuda, A. Chainani, and S. Shin, Science 332, 564 (2011).
